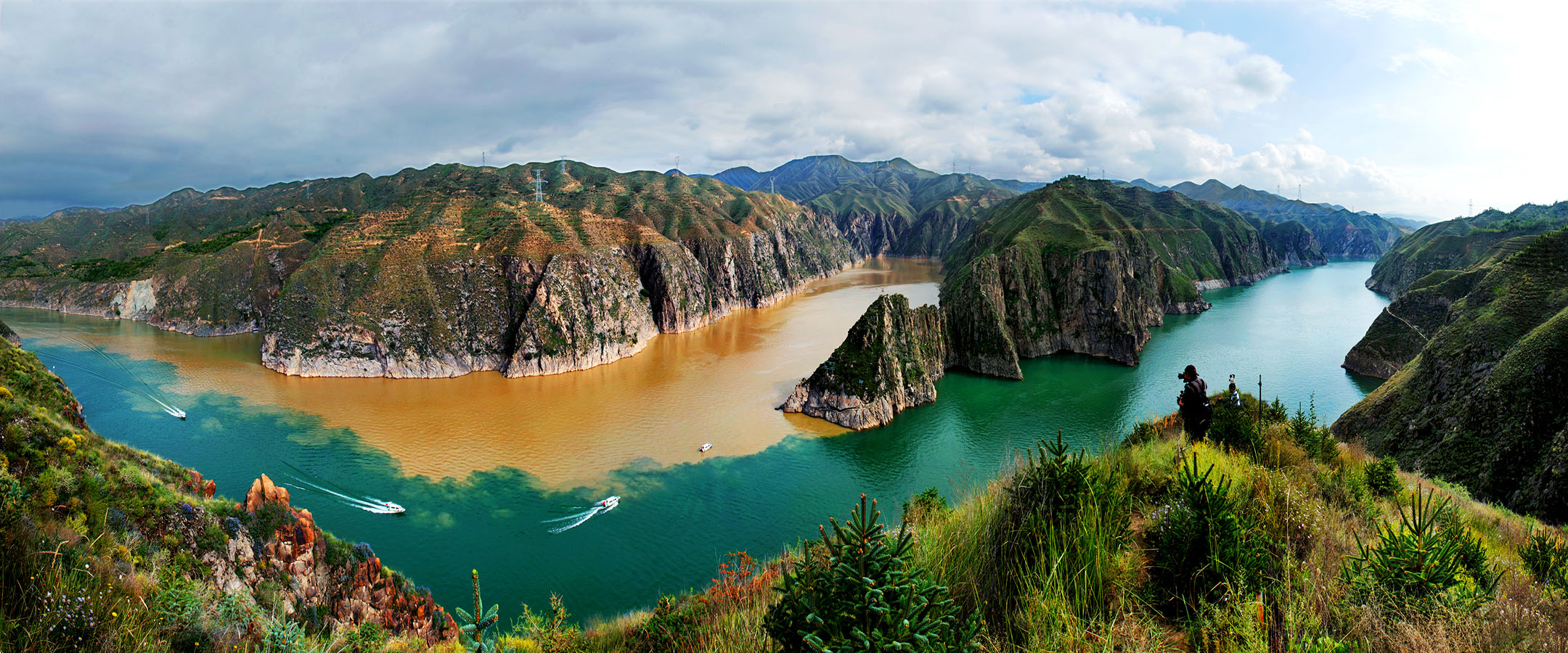
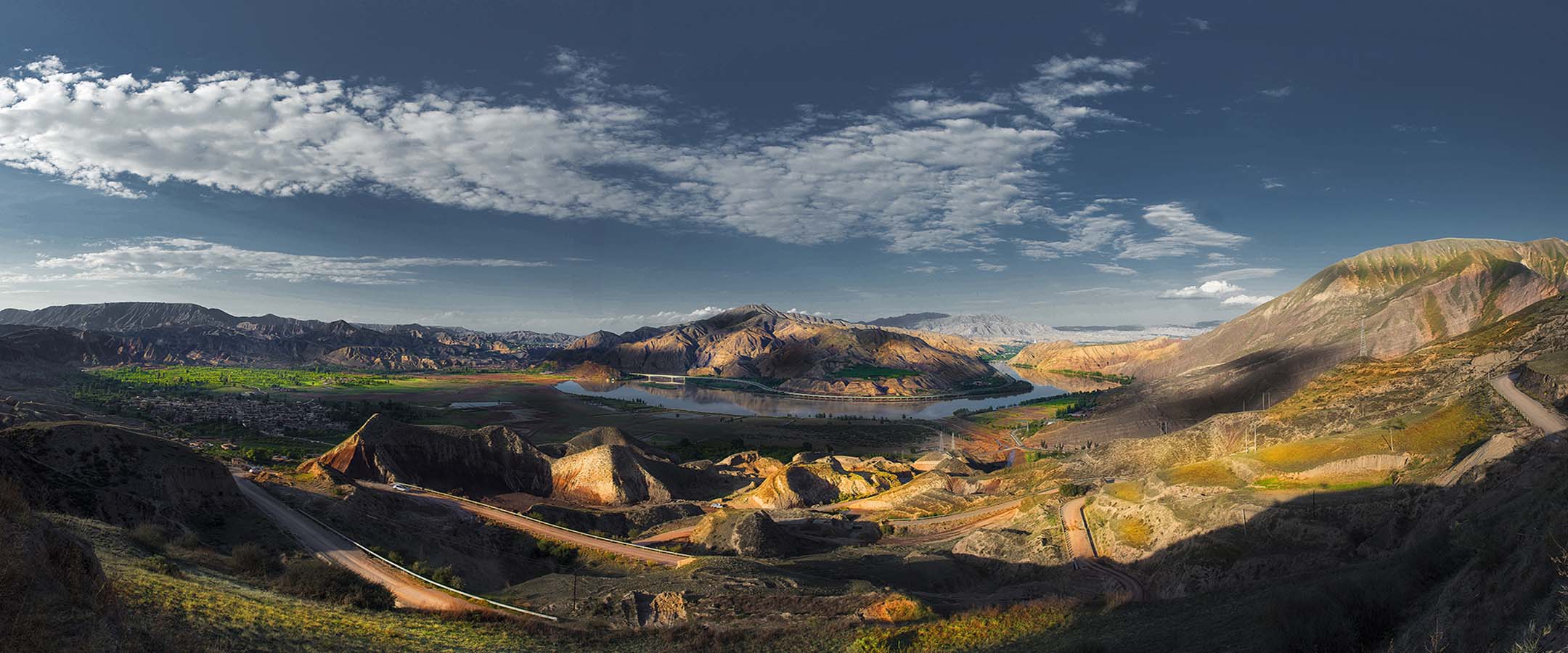
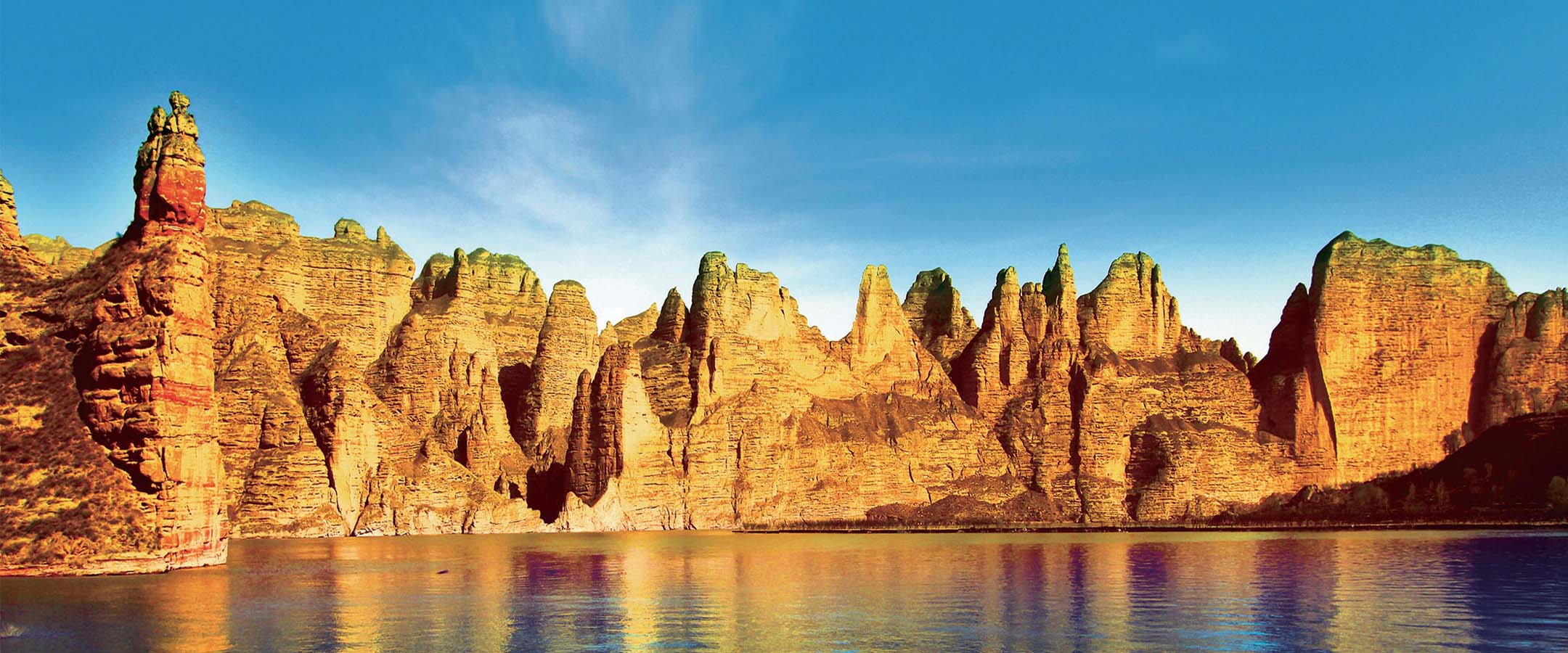
由于黄河和湟水的切割,在黑方台形成一个东西长约 10.7km、南北宽约 1-3km 的黄土台塬地貌。黑方台台地高出周围地形约 100-133 米,长期的大水漫灌引起黑方台边坡失稳而反复发生滑坡。黑方台台塬自 1968 年以来共发生大小滑坡 107 次,共发育有 21 处黄土滑坡和 14 处黄土—基岩滑坡,两类滑坡总体积分别约 1304.7×104m3 和 3300.90×104m3。如今黑方台是我国黄土区两类典型滑坡的重点监测和研究点,曾多次成功预测滑坡发生。
Due to the cutting of the Yellow River and Huangshui River, a loess tableland with a length of 10.7km from east to west direction and 1-3km from south to north direction is formed in Heifangtai. The Heifangtai tableland is about 100-133 m higher than the surrounding terrain. The long-term flood irrigation caused the slope instability and repeated landslides. Since 1968, there have been 107 large and small landslides in Heifangtai tableland, including 21 loess landslides and 14 loess-bedrock landslides. The total volume of the two types of landslides is about 1304.7 ×104 m3 and 3300.90 × 104 m3 respectively. Nowadays, Heifangtai is the key monitoring and research site of two typical landslides in loess area of China. And it has successfully predicted the occurrence of landslides for many times.