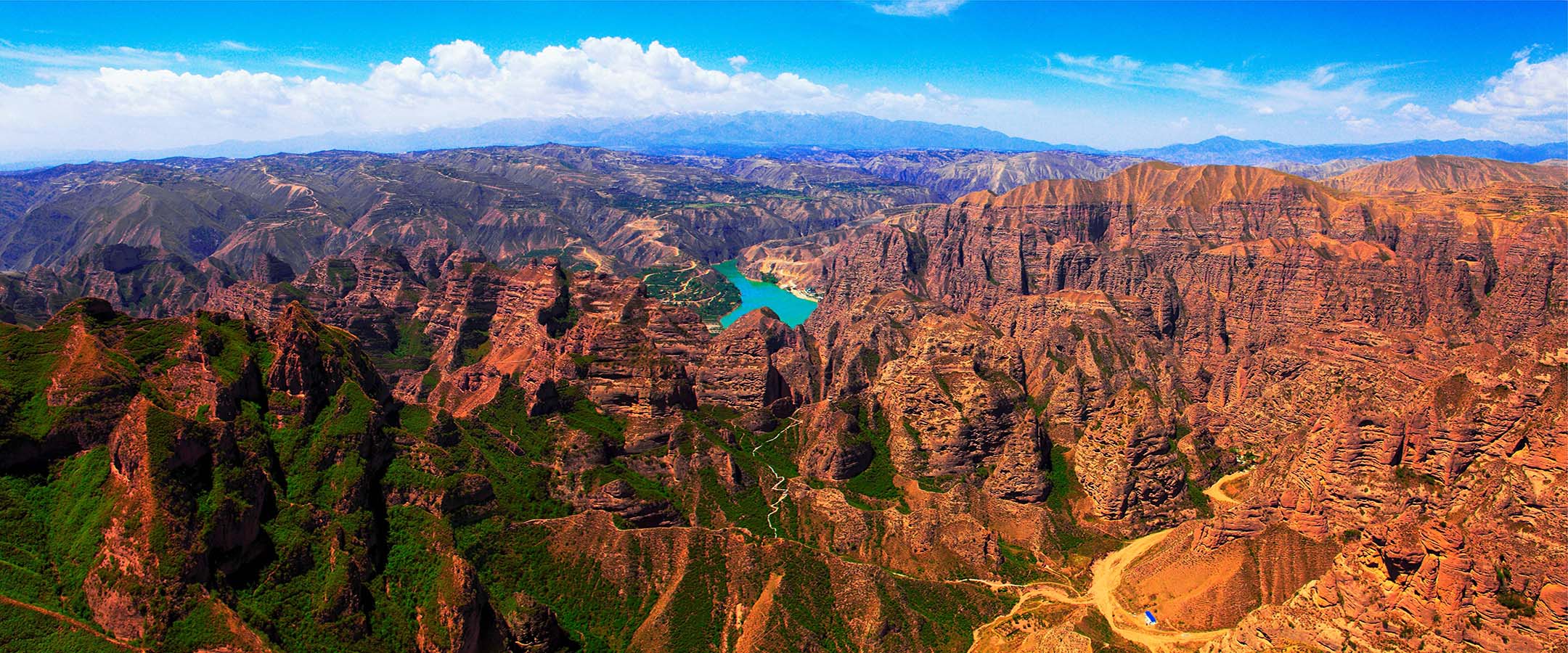
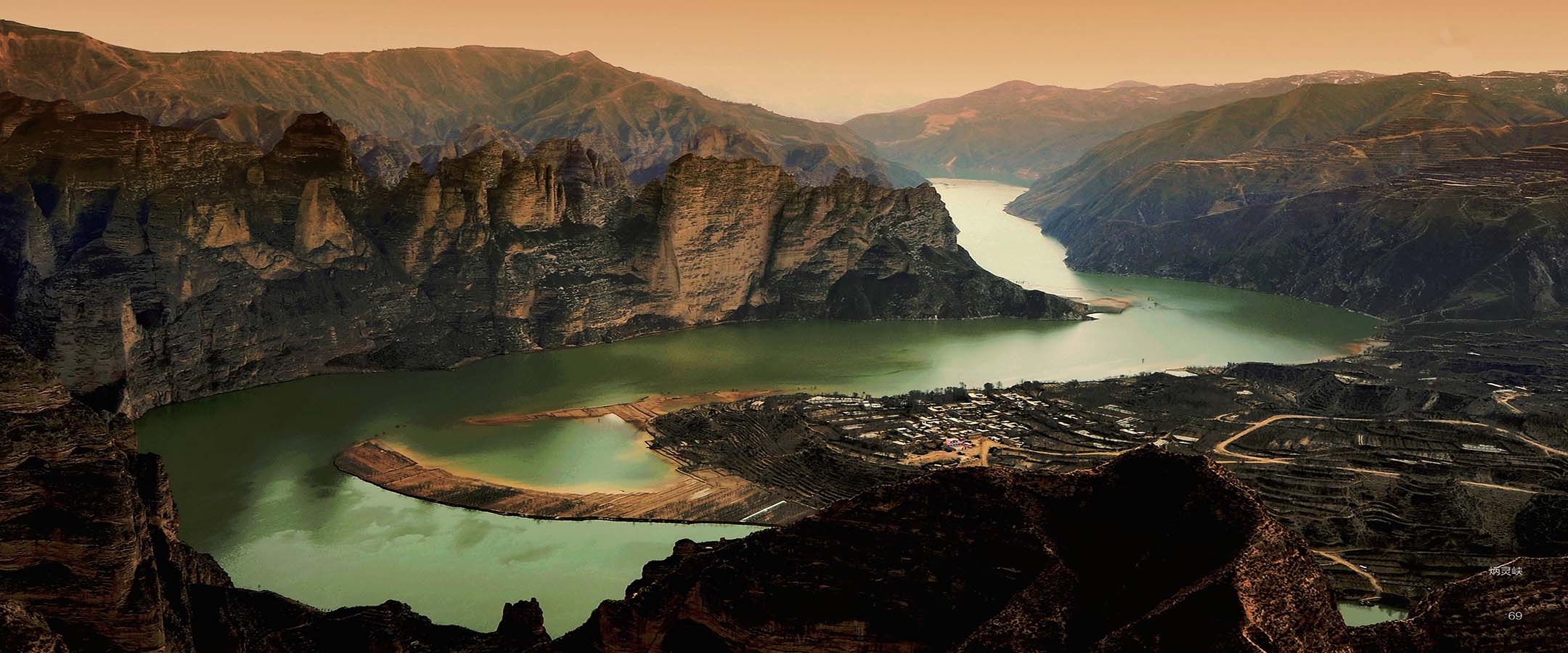
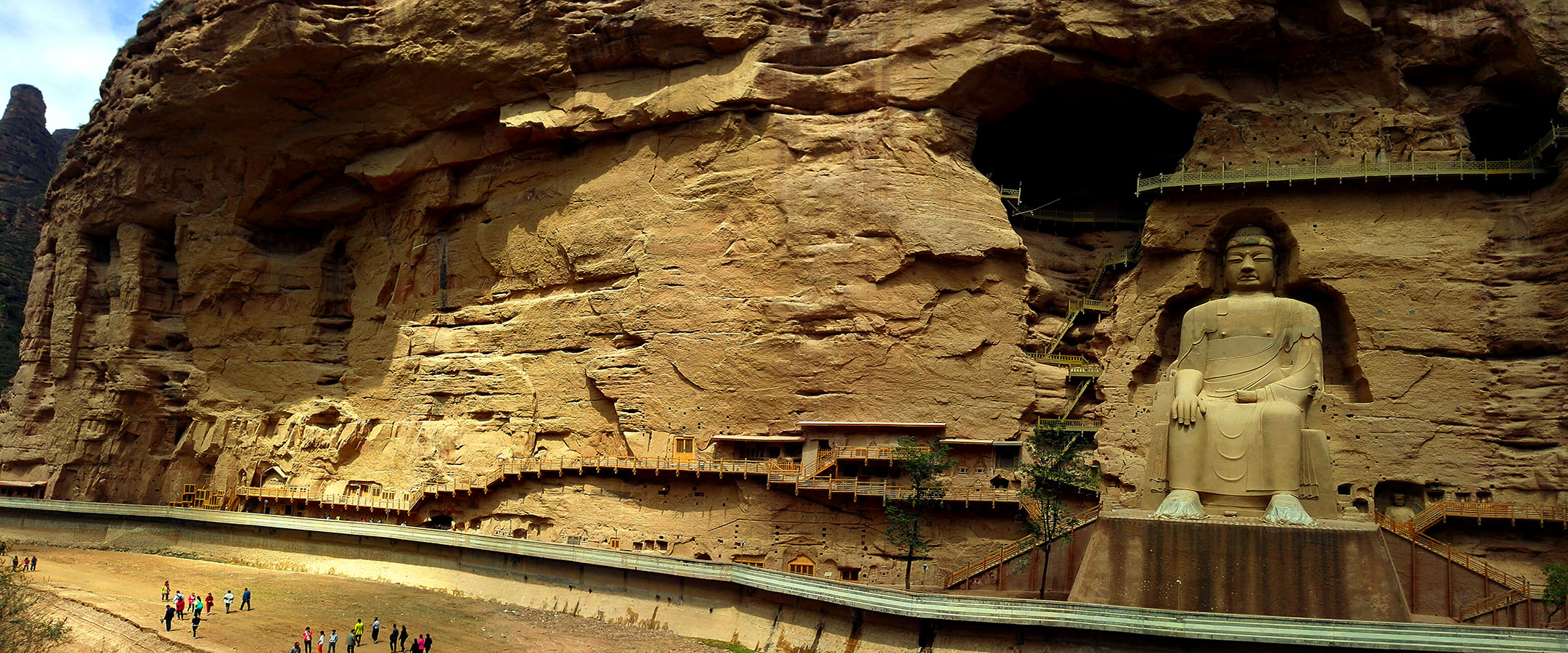
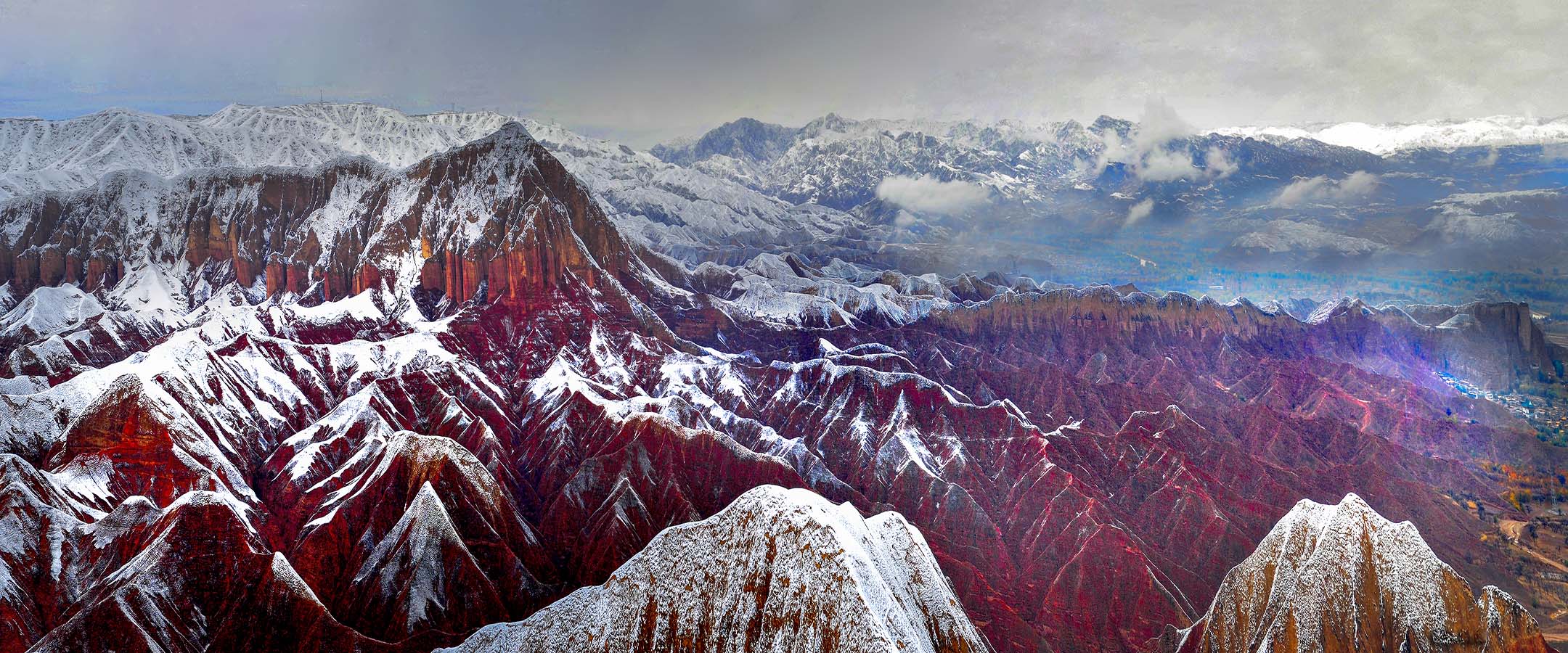
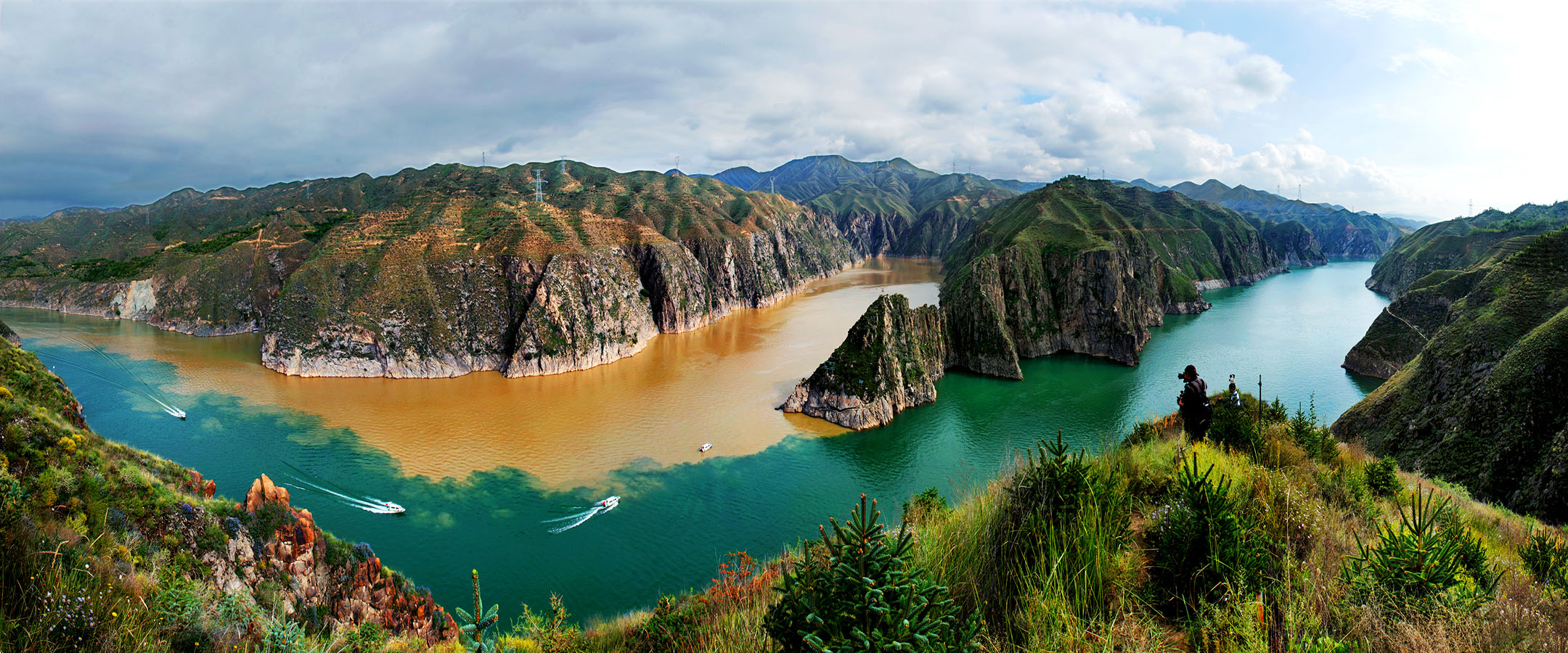
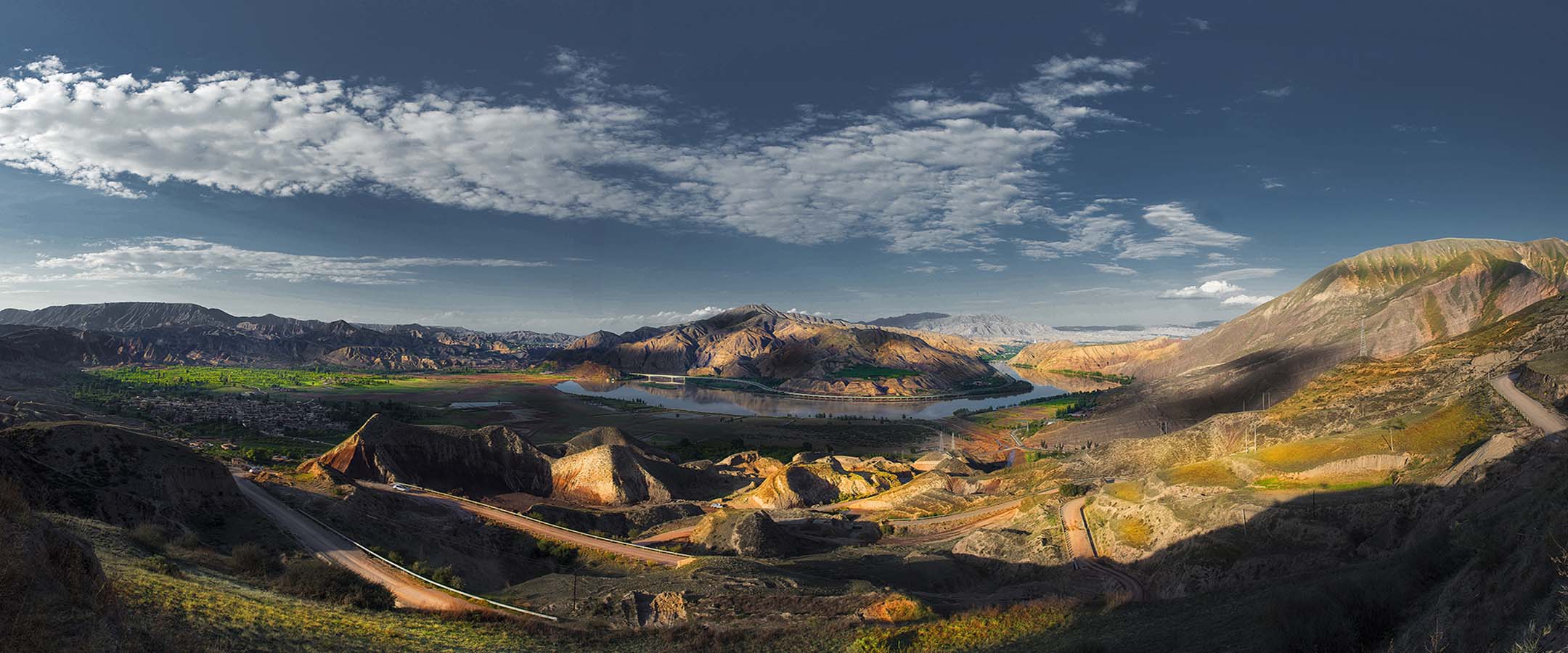
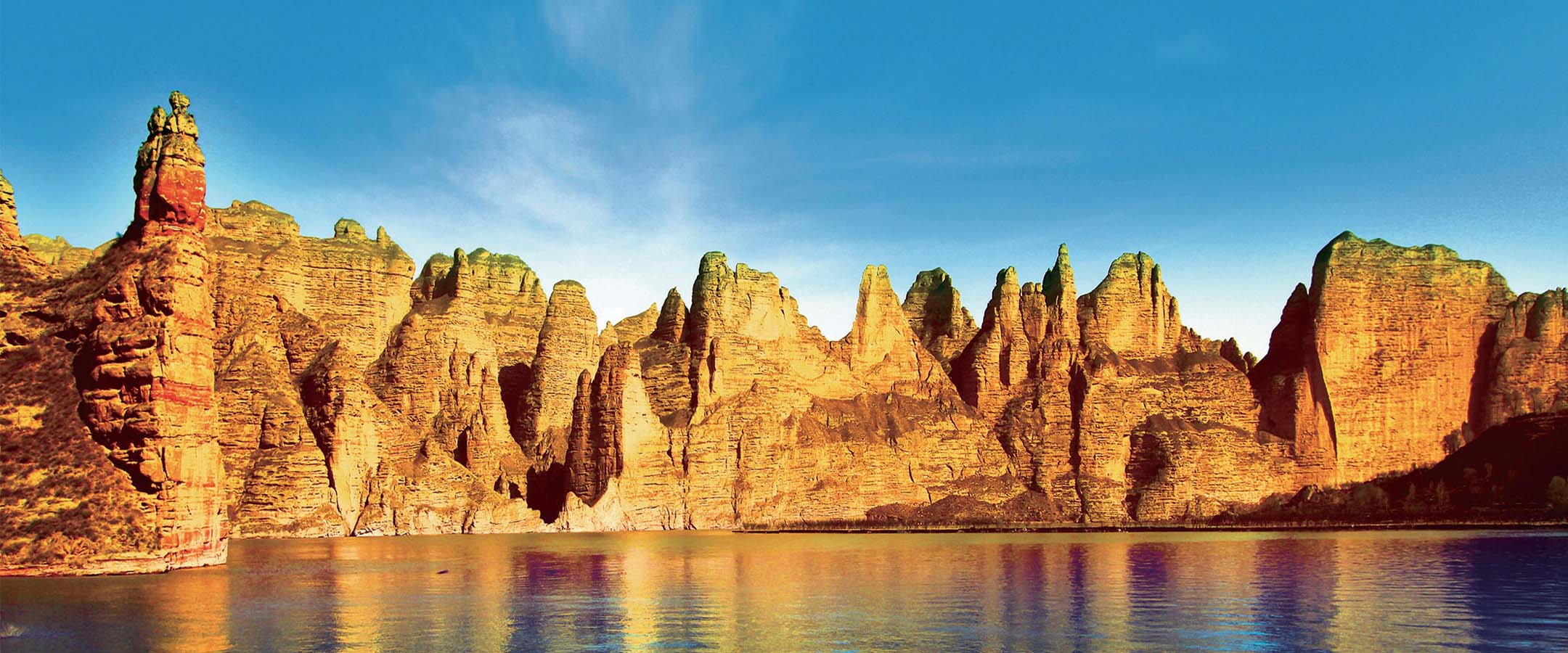
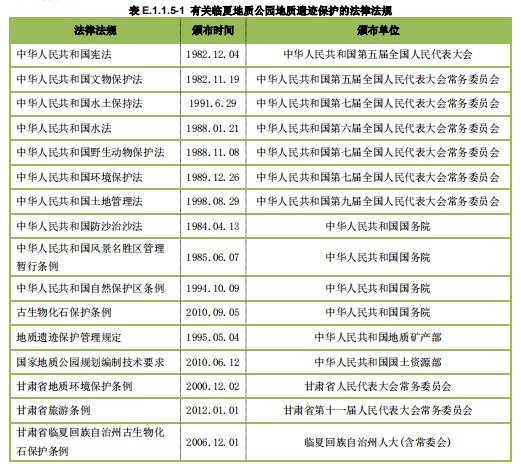
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.
Mr.