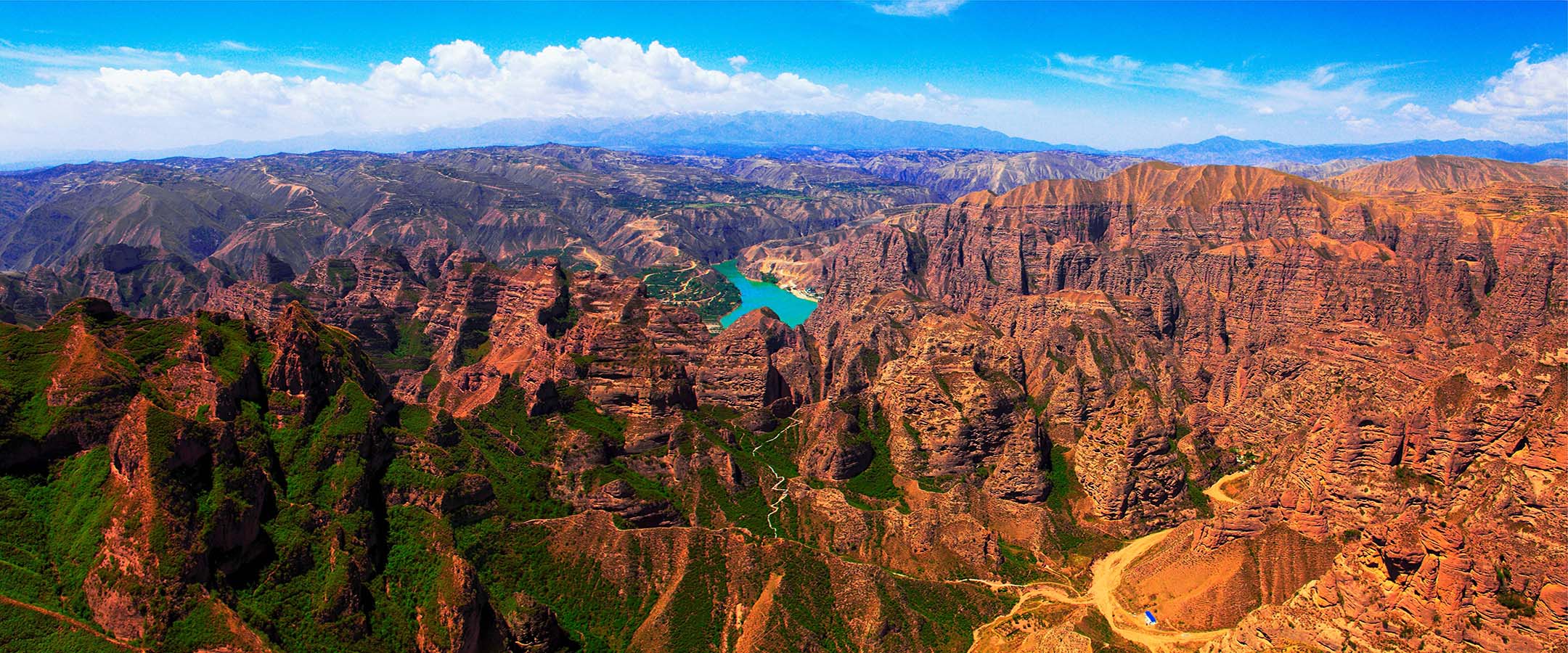
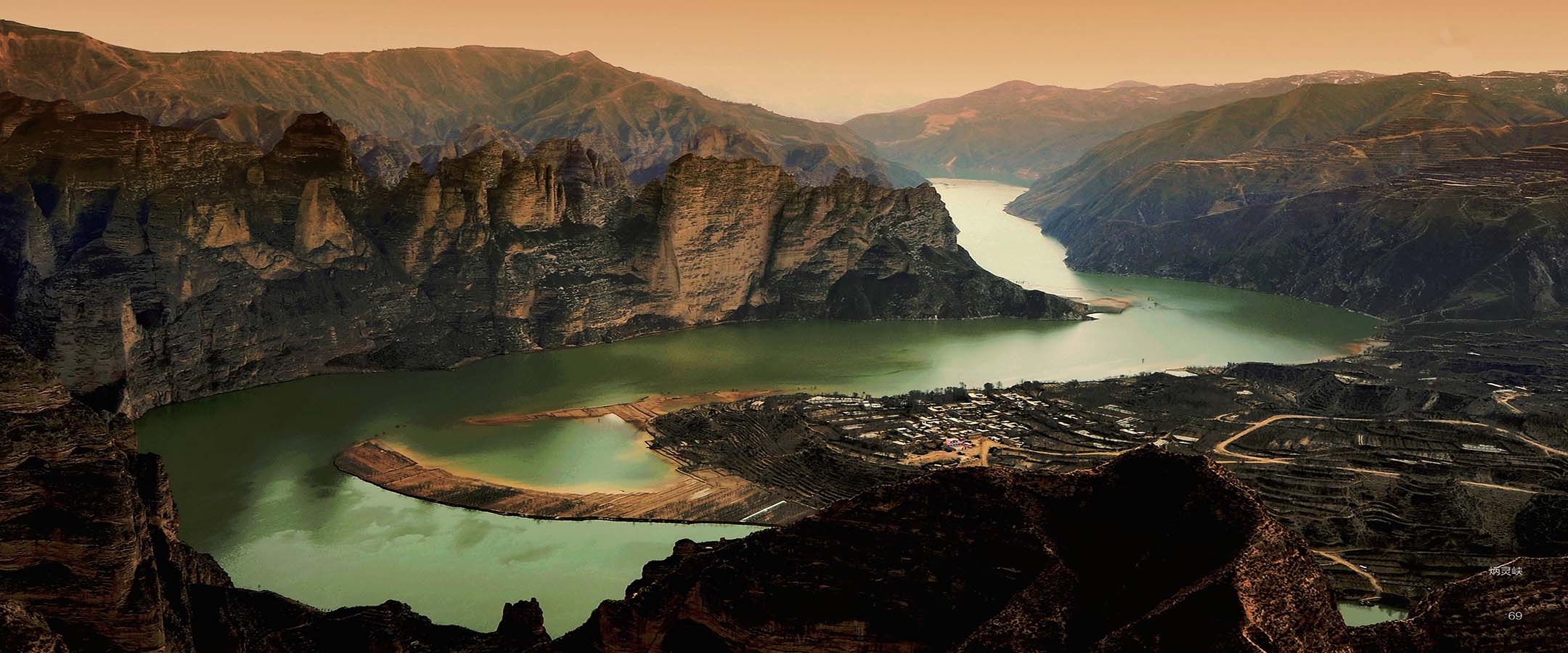
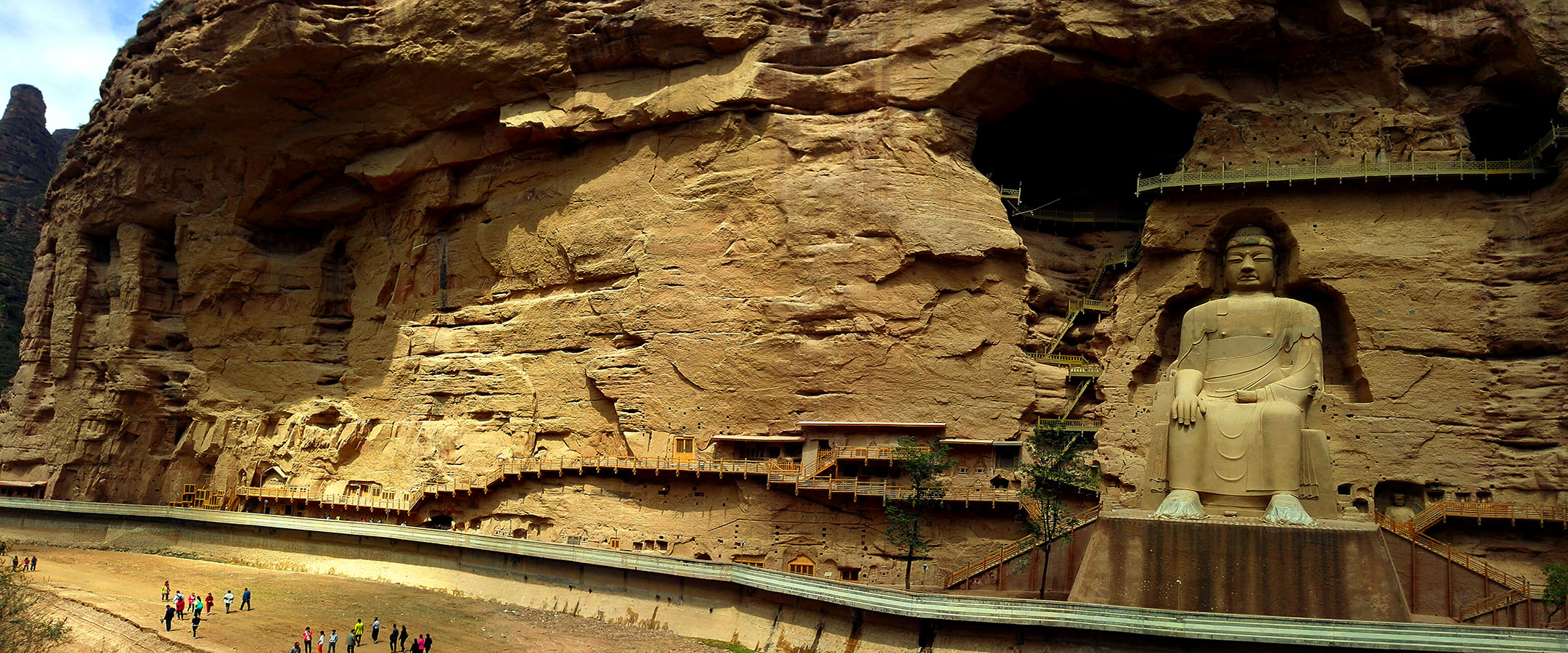
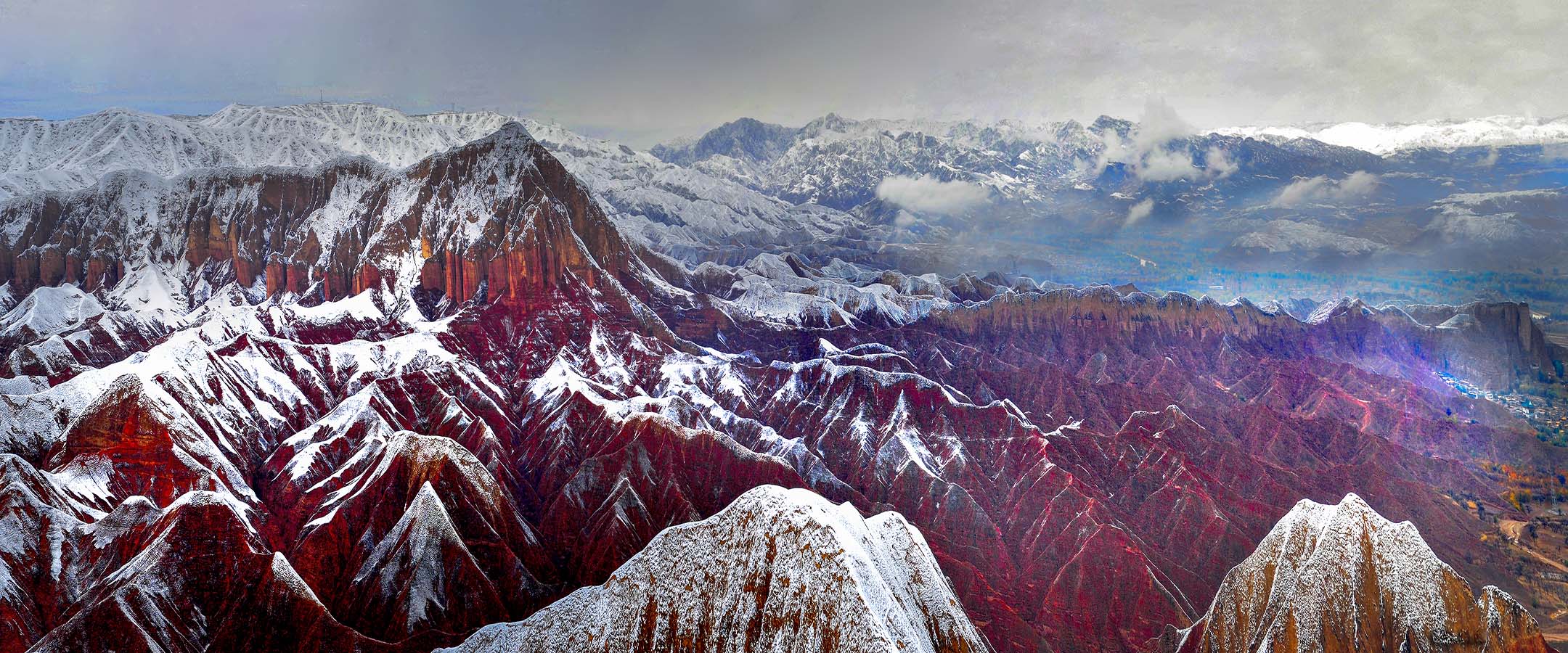
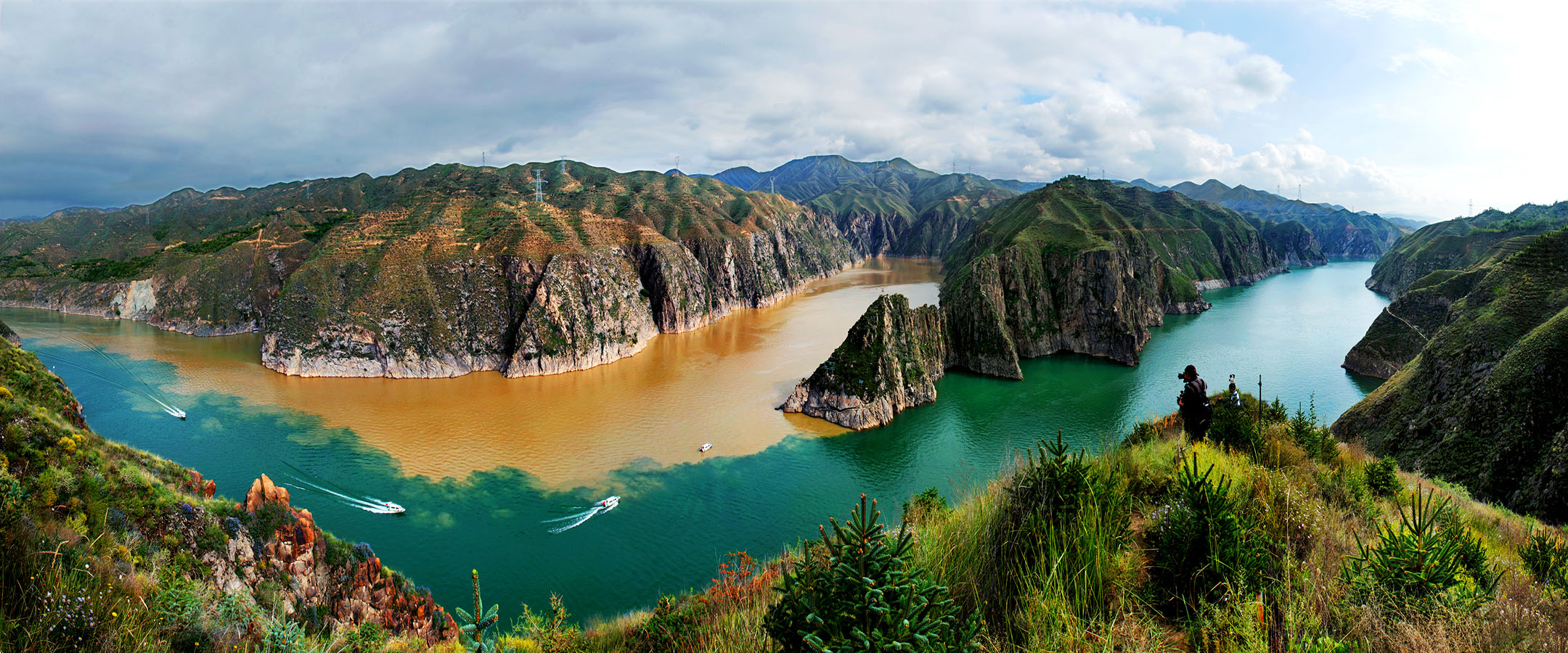
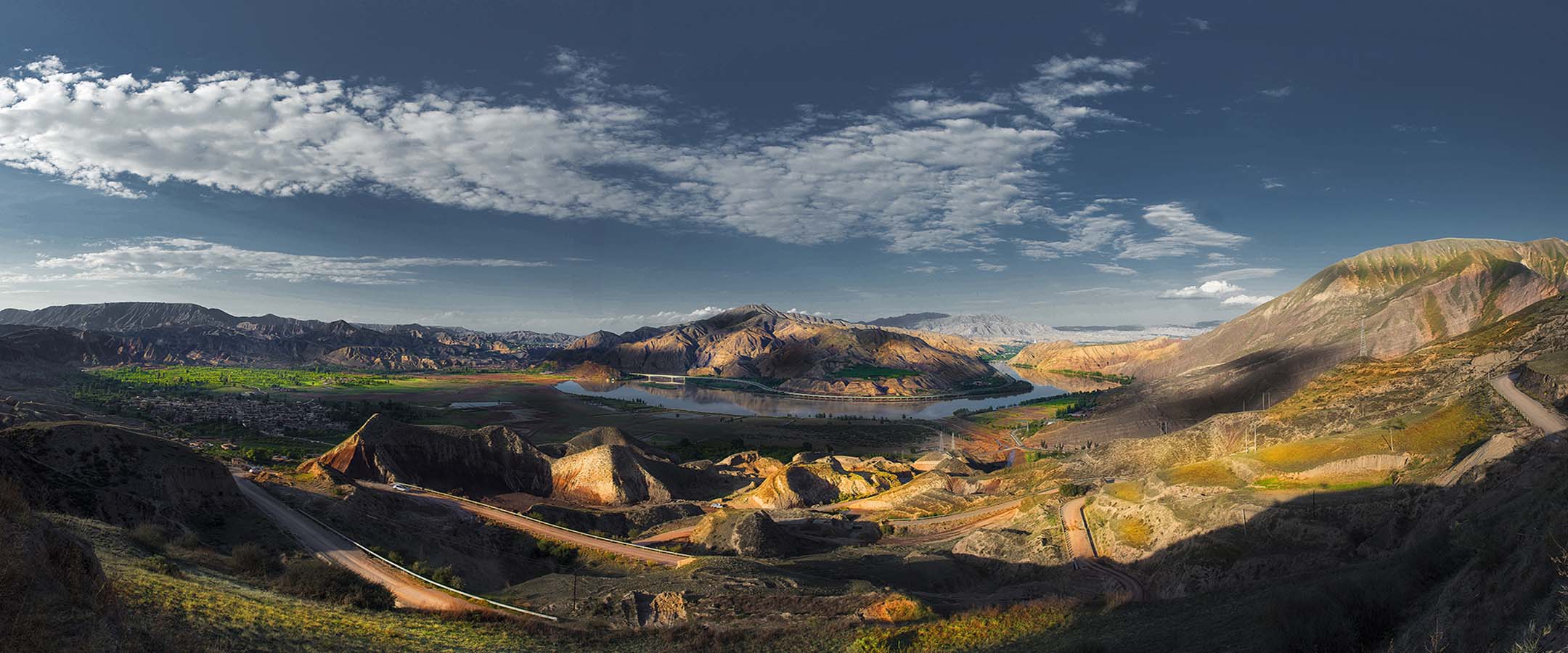
始建于西秦建弘元年(420)的炳灵寺,是首批全国重点文物保护单位之一,与莫高窟、云冈石窟、龙门石窟、麦积山石窟等并称为中国十大石窟。炳灵寺最早称为“唐述窟”,唐代称“龙兴寺”、“灵岩寺”,北宋始称“炳灵寺”。“炳灵”为藏语“仙巴本郎”的音译,意为“十万佛洲”。炳灵寺由上寺、下寺、洞沟、野鸡沟和佛爷台等部分组成,包括石窟、雕刻、壁画、寺庙等,为一处重要的佛教艺术胜迹。
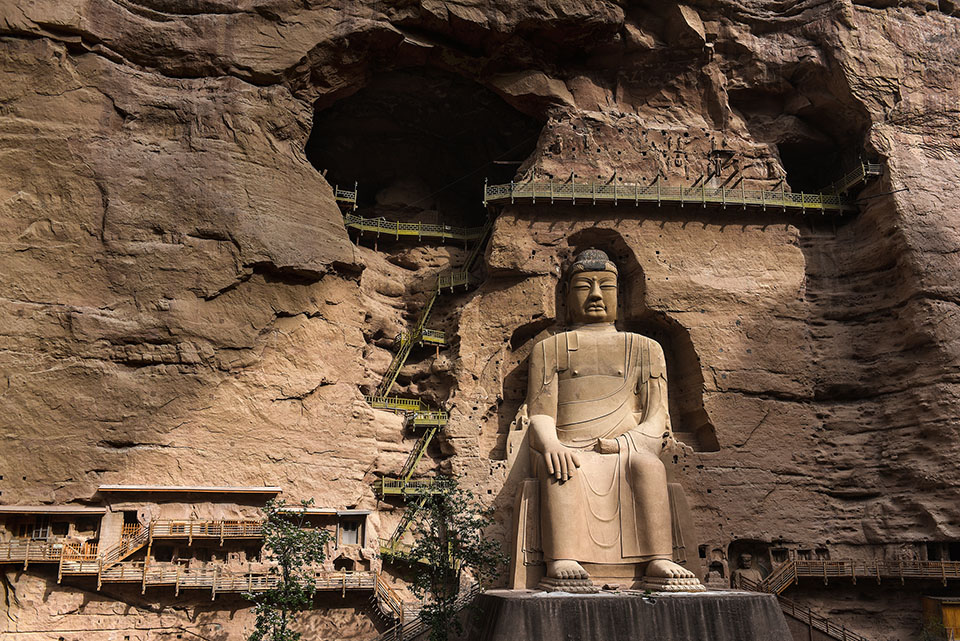
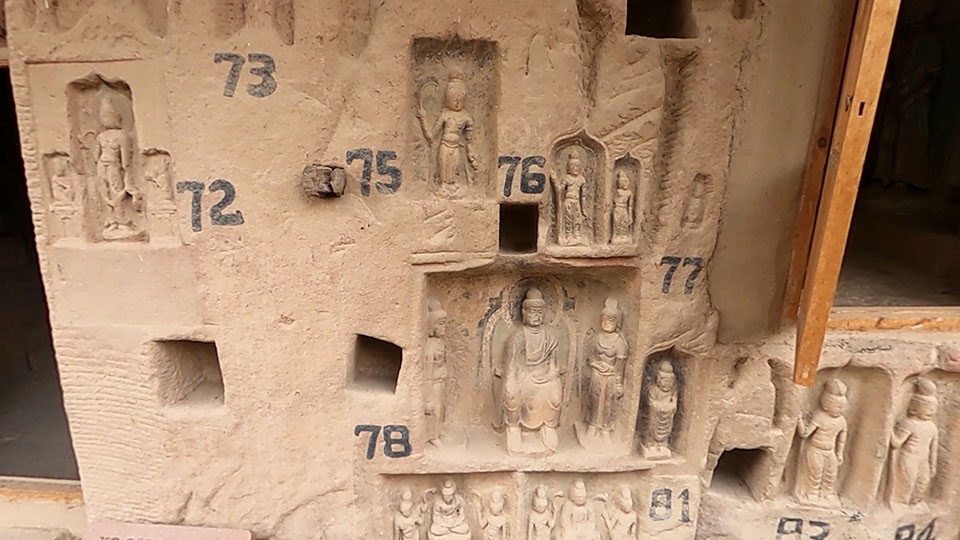



在上寺以东还有数处唐代僧人居住遗址,仅存残垣,由此可见历史上炳灵寺规模之大。
Initially established in 420, Binglingsi Grottoes is one of the first National Major Cultural Relics Preservation Units. It belongs to the top ten grottoes in China together with Mogao Grottoes, Yungang Grottoes, Longmen Grottoes and Maijishan Grottoes. In the North Song Dynasty(960-1127), it was named Binglingsi Grottoes. Bingling is a transliteration of Tibetan,which means Ten Thousand Buddhas. Binglingsi Grottoes consists of upper temple, lower temple, caves, Yeji valley and the Buddha's altar. It is an important Buddhist art site including grottoes, murals and temples.
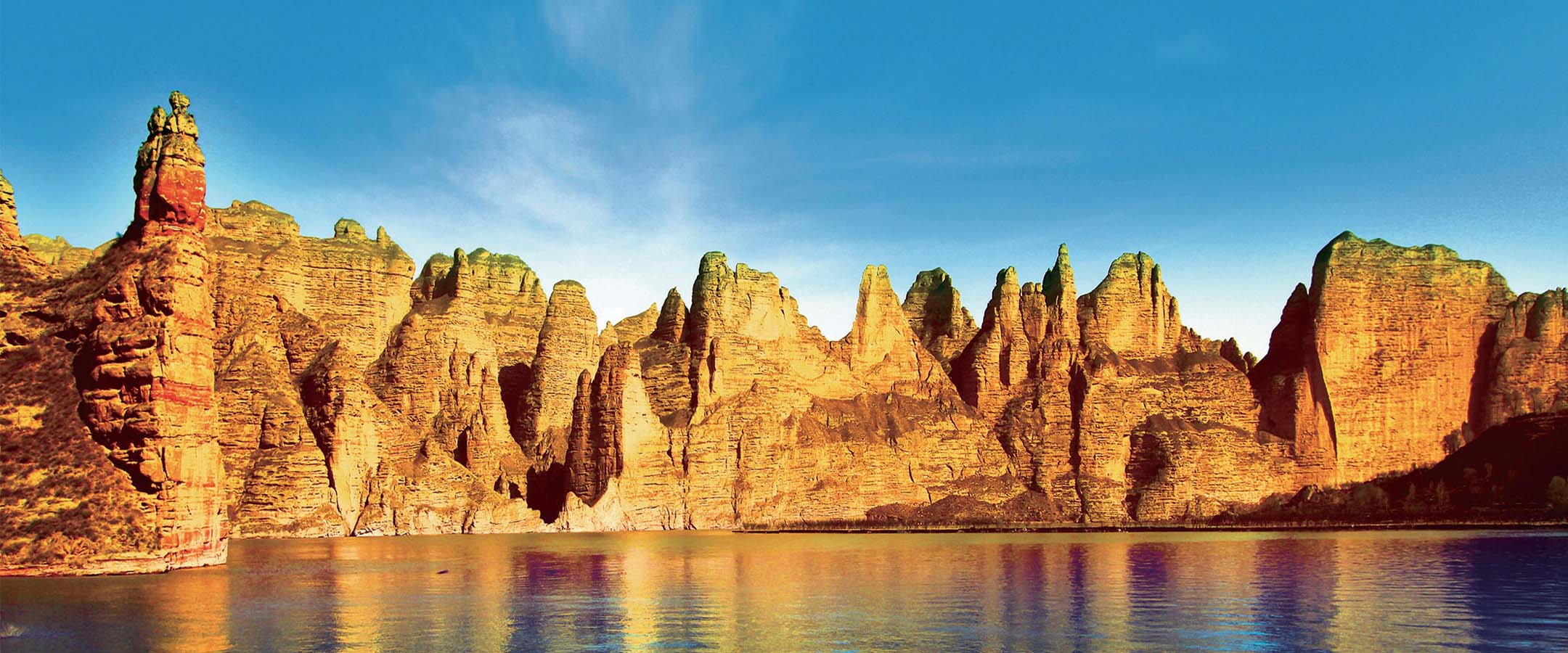
Built in Western Qin Dynasty (420), Binglingsi Grottoes was expanded and renovated several times through ages. There are 216 grottoes in total today, mainly in the lower temple. The grottoes are distributed on the cliff of Cretaceous Hekou Formation glutenite, extending 1 kilometer from south to north on the bank of the Yellow River. The lower temple has 195 grottoes,which are of rare and unique shape.
Around 1000 square kilometers’ murals are well-preserved in the Binglingsi Grottoes. All murals present superb painting arts.
Surrounded by mountains, the upper temple is composed of the main assembly hall, the main hall, the gate, the monk house. There are preserved stone statues, clay statues, bronze statues, sutras, Thangka, and musical instruments in the upper temple. It used to be an important place of conducting religious activities for followers nearby. And precious cultural relics are found in the Zhuoma Cave of the upper temple. These cultural relics are of important religious and historic value.
Several living ruins of monks from the Tang Dynasty still exist in the east of the upper temple, which are the evidence of its past prosperity.